4. Stanley Eyelock Nano NXT
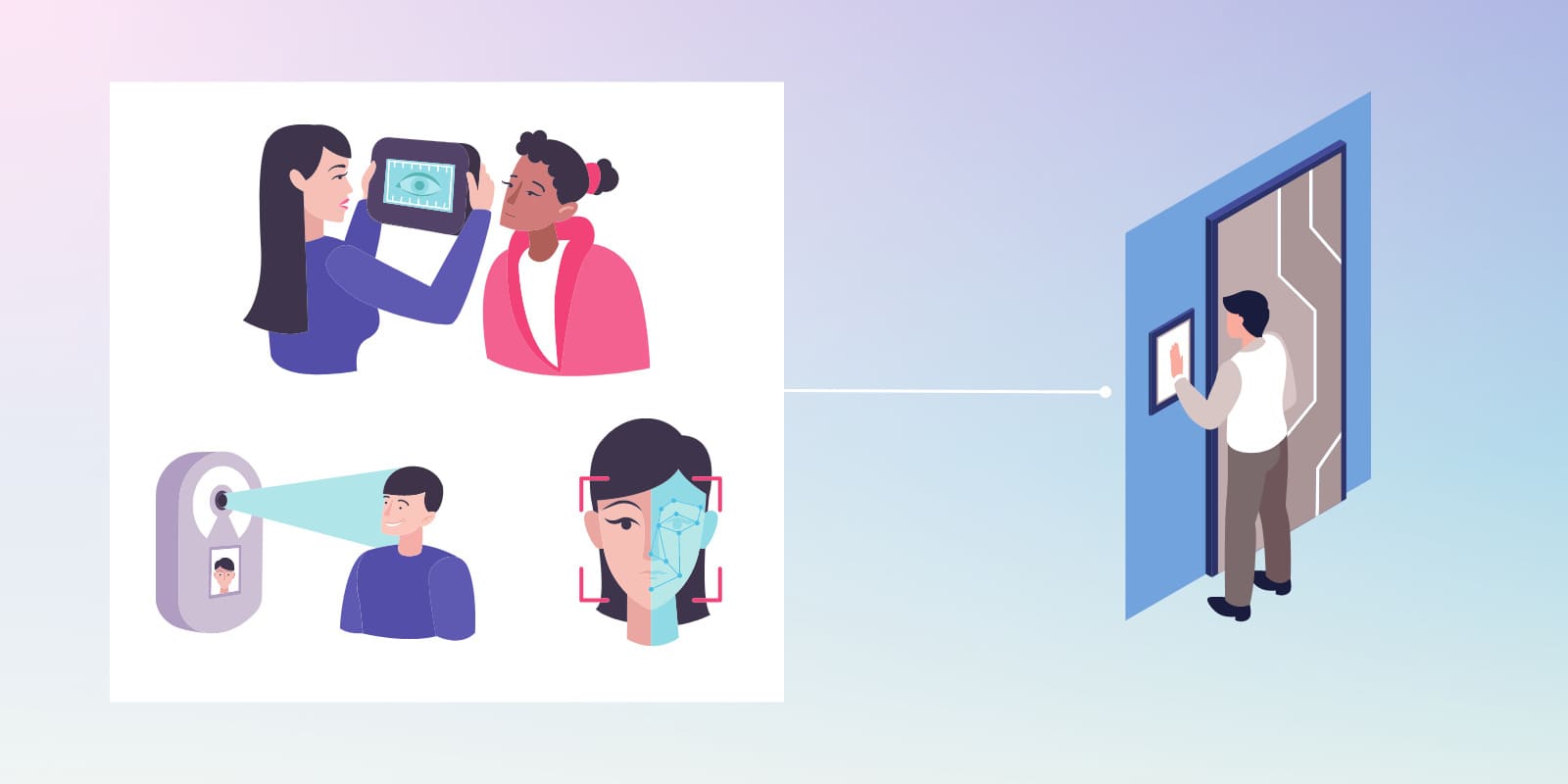
The Stanley Eyelock nano NXT is a biometric control machine that uses up to 240 unique iris characteristics to create a unique code to identify employees. The device encrypts this code and stores it on the device or a server. When someone looks into the scanner, the algorithm checks if the person’s iris characteristics match any encrypted records before it opens the door.
While this technology isn’t completely foolproof, the company guarantees a minimal false acceptance rate of only one in every 1.5 million irises scanned wrong. You can equip the nano NXT with a two-factor authentication system by adding a third-party card reader.
This biometric control uses a bank-grade encryption system that you can easily integrate with other access control and attendance platforms. You can easily configure the nano NXT to work with your current application by using your personal browser and many programming languages. The software development kit is available on C# (.NET), C / C++, and Java.
Manufactured by Stanly, you can easily integrate the nano NXT with other Stanly products you use in your business. The biometric devices provide a quick authentication process, authenticating as many as 20 people per minute. It can also accurately identify people when they move past it rather than standing in front of the device when scanning.
With a UL-294 certification, the Stanley Eyelock Nano NXT device has been tested to ensure it’s reliable, secure, has standby power, possesses high material endurance, and can withstand attack or attempts to destroy it. The model also complies with international standards, including those of Canada, the US FCC, and the European Union.
The Stanley Eyelock Nano NXT is one of the top biometric access control devices that uses iris recognition rather than fingerprint patterns.